
AI Search Response
Continue your AI search

Key ovarian cancer information
-
Early symptoms of ovarian cancer are often subtle and easy to overlook. They include bloating and crampy aches that feel similar to period cramps but don’t follow a monthly cycle. You may also feel like you need to urinate urgently and more often than normal.
-
How common is ovarian cancer? It’s fairly rare, affecting one in 91 women.
-
The average age of an ovarian cancer patient at diagnosis is 62 years. Two-thirds of women are diagnosed after age 55, once menopause has ended.
-
Ovarian cancer is the most deadly type of cancer among women, often because it’s found so late. 75% of women are first diagnosed when the disease is already in an advanced stage.
-
There are many possible ovarian cancer causes. Factors that increase your risk include inherited genetic issues and environmental factors like chemical exposure to talcum powder or hair relaxer.
Find out if your ovarian cancer was caused by exposure to a dangerous product
“Studies have linked an increased risk of developing ovarian cancer to long-term use of talcum powder or chemical hair relaxers. If you’ve been diagnosed with ovarian cancer and have a history of use with either product, you may be able to file a lawsuit and seek compensation. Use the links below to see if you qualify.”
Learn more about the connection between ovarian cancer and common products:
— Jamie Pfeiffer, JD, Medical Contributor
What is ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a form of cancer that forms in the small organs found in the lower abdomen, called the ovaries. The ovaries produce eggs and certain hormones. Sometimes, abnormal cells in the ovaries start growing out of control and can then spread to other parts of the body.
Finding this kind of cancer early is difficult. Many women don’t recognize the warning signs of ovarian cancer. If you’re diagnosed with ovarian cancer early, it’s more likely to be treatable, which can lead to a better outcome. You can get ovarian cancer at any age, but it’s more common in women over the age of 55.
There are three main types of ovarian cancer:
-
Epithelial ovarian cancer grows on the outer covering of the ovary. Between 85%–90% of ovarian cancers are this type.
-
Germ cell cancer starts in the cells that produce eggs inside the ovaries. It’s more common in younger women and accounts for about 5% of ovarian cancers.
-
Stromal cancer starts in the cells that hold the ovary together and produce hormones. It’s very rare.
It’s important to keep an eye out for symptoms and get checked if you have concerns or known ovarian cancer risk factors.
More information about ovarian cancer

Diagnosed with ovarian cancer
Start by learning about your type and stage of ovarian cancer and what to expect after your diagnosis, including your different treatment options.

Dealing with the costs of ovarian cancer
Treating ovarian cancer is often expensive. If your cancer is linked to exposure to a dangerous product, you may have options to help cover these costs.

Caring for someone with ovarian cancer
If a loved one has been diagnosed with ovarian cancer, you can help them learn about their options and support them through treatment.
Early warning signs of ovarian cancer
Many women don’t experience noticeable ovarian cancer symptoms. It’s easy to mistake them for a stomach ache or cramps from your period. However, unlike menstrual cramps, the pain from ovarian cancer doesn’t follow a monthly cycle.
Younger women who are still having regular periods may notice other symptoms like swelling, pain or unusual bleeding. Older women who are approaching or have gone through menopause might notice bloating, feeling full after eating small amounts of food and changes in bowel movements or urination. In both cases, symptoms don’t go away on their own, and they slowly worsen over time.
If you notice the warning signs of ovarian cancer at any age, it’s always worth getting checked out by your doctor. The earlier you find the cancer, the more treatment options you have and the better your prognosis will be.

What are the most common ovarian cancer symptoms?
Many ovarian cancer symptoms are general and easy to overlook. This can make it difficult to diagnose the disease in the early stages. If you experience these common ovarian cancer symptoms, it’s best to take them seriously and get evaluated by your doctor. This is especially true if you’ve been in contact with talcum powder, chemical hair straightener or other chemicals that have been linked to increased ovarian cancer risk.
Your ovarian cancer symptoms will likely vary depending on whether you have begun perimenopause or gone through menopause. You might notice different changes if you’re younger and still have your period.
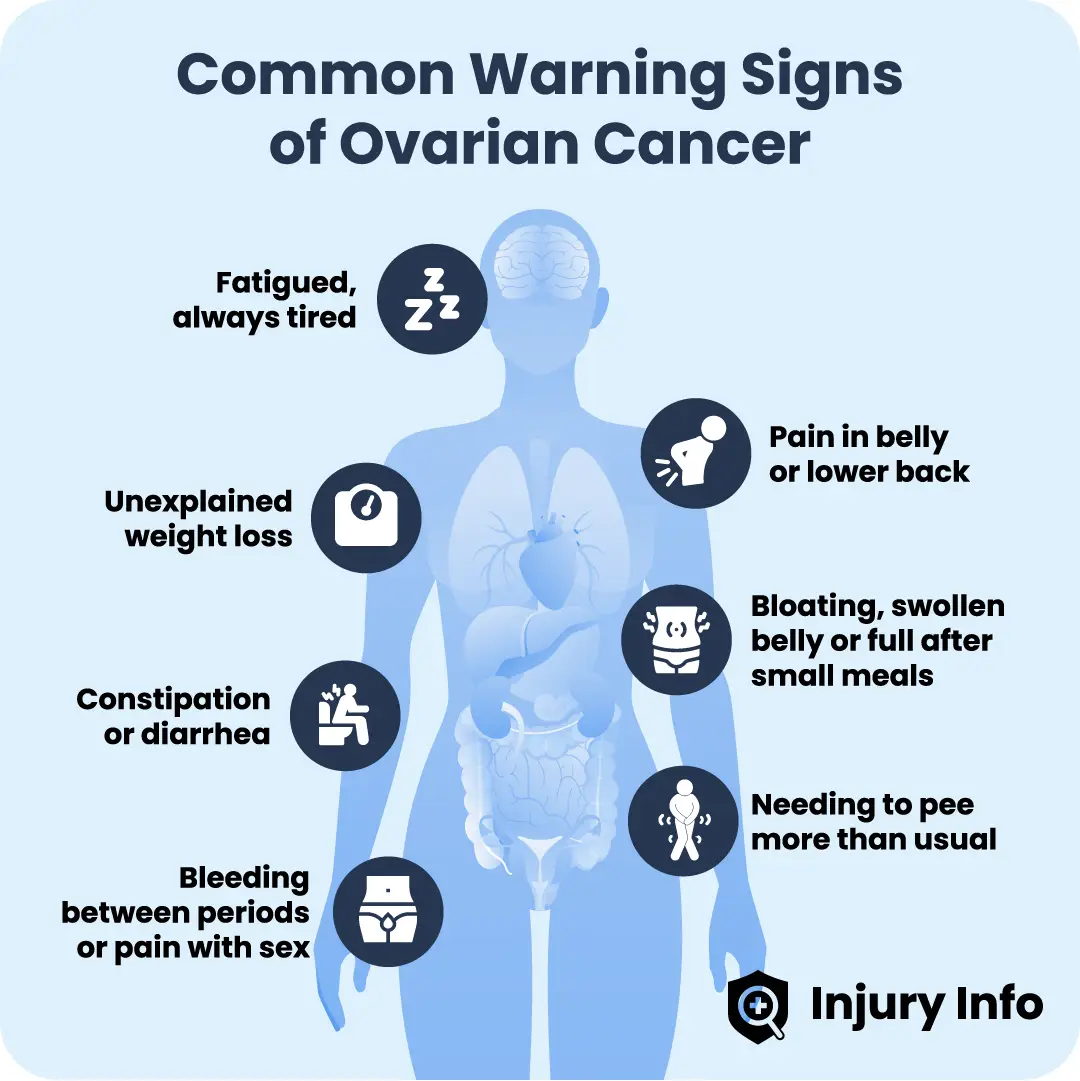
No matter your age, it’s important to contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of these ovarian cancer signs more than 12 times a month:
-
Bloating and swelling.
-
Feeling tired or fatigued for no reason.
-
Pain in your back, stomach or abdomen.
-
Feeling full without eating much.
-
Constipation or diarrhea.
-
Frequent urination.
-
Unexplained weight loss.
-
Pain during sex.
-
Vaginal bleeding that’s irregular or very heavy.
Pre-menopausal signs of ovarian cancer
Younger women are less likely to get ovarian cancer, but it’s possible. Exposure to certain chemicals increases your risk. If you’re younger and regularly get your period, you might notice symptoms like:
-
Swelling in your belly area and feeling unusually full.
-
Cramps that are similar to the ones you get during your period.
-
Digestive issues like constipation or diarrhea.
-
Needing to urinate more often than usual.
-
Losing weight without trying.
-
Bleeding when it’s not your period or heavier than normal bleeding.
-
Pain during sex that you haven't experienced before.
Ovarian cancer during perimenopause
If you’re older (in your late 40s) but still sometimes getting your period, you might be going through changes to your menstrual cycle that lead up to your period stopping completely. In medical terms, you’re in perimenopause. During perimenopause, common ovarian cancer symptoms include:
-
Bloating and swelling.
-
Pain and cramps in your abdomen.
-
Feeling full, even if you don’t eat much.
-
Feeling like you have to urinate often, even if you just went.
-
Bleeding between periods and after having sex.
Symptoms of ovarian cancer after menopause
When your monthly periods stop completely, this is called menopause. When you haven't had a period for more than twelve consecutive months, you’re considered "post-menopausal." This menopausal transition period usually happens after age 50. Common ovarian cancer symptoms during this time include:
-
Bloating and swelling in your belly that you can’t explain.
-
Cramps and pain in your belly that do not go away or that come back often.
-
Constipation or diarrhea.
-
Having to urinate frequently.
-
Losing weight without a reason.
-
Vaginal bleeding, which can be light or like a heavy period. Because you no longer have a period in menopause, it’s important to talk to your doctor right away if you notice any bleeding.
Who does ovarian cancer affect?
Ovarian cancer can affect women at any age, but it’s relatively rare in younger women. Studies have shown that people who use products like talc powder and hair relaxer may get ovarian cancer at higher rates than people who don’t use these products.
Who is most likely to be affected by ovarian cancer? Here are some of the known risk factors:
-
Age: The older you are, the higher your risk. Most women who are diagnosed are over age 63.
-
Race: White women have a slightly higher risk of developing ovarian cancer than women of other races. However, black women are more likely to get diagnosed later and have alower 5-year survival rate.
-
Genetics: Having a family member with ovarian cancer can increase your chances of developing the disease.
-
Estrogen therapy: Using hormone replacement therapy can increase ovarian cancer risk.
-
Medical history: Having other medical issues, such as endometriosis, may cause an increased risk of ovarian cancer.
-
Talcum powder use: Using talcum powder in your genital area for a long time can expose you to chemicals that have been linked to an increased risk of ovarian cancer.
-
Use of certain hair products: Using hair relaxer products that contain certain chemicals may increase your cancer risk, especially if you started using these products at a young age.
Could using talcum powder or hair relaxers be linked to your ovarian cancer?
“Some research shows a possible link between ovarian cancer and long-term use of talcum powder or chemical hair relaxers. These products may affect the body in ways that increase cancer risk. If you’ve been diagnosed, you may be able to take legal action.”
Learn more about the potential connection between ovarian cancer and common products:
— Dr. Danielle K. Miller, DNP, MSN, BSN, RN, Medical-Legal Content Specialist & Healthcare Strategist
How do you get ovarian cancer?
Using certain products may increase your risk of getting ovarian cancer. Research has linked contact with specific chemicals to increased risks of developing the disease. Your risk is higher if you have used these products for a long time.
-
Users of chemical hair relaxers: The groundbreaking Sister Study found that frequent use of chemical hair relaxers—over four times a year—was linked to an increased risk of ovarian cancer. The younger you start using these products, the higher your risk may be. Learn more about the potential links between ovarian cancer and hair relaxers.
-
Hair stylists and cosmetologists: Because hair care professionals use chemical hair relaxers and hair dye daily, they’re exposed to the potentially carcinogenic chemicals in these products more frequently and for longer periods of time.
-
Those using talcum powder for personal hygiene: Baby powder and personal care powder containing talc may be contaminated with asbestos. Women who have used powder in their genital areas as part of their regular hygiene practice may have a higher risk of ovarian cancer. Learn more about ovarian cancer and talc use.
-
Users of products made with PFAS:A wide variety of products are made with per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), including non-stick pans, fabric stain-protector sprays, fire-resistant clothing and various plastic tools. Exposure to these chemicals has been linked to an increased risk of ovarian cancer.
How is ovarian cancer treated?
For most people, ovarian cancer treatments include a combination of surgery and chemotherapy. Your doctor may remove one or both ovaries, your uterus and other tissues nearby if the cancer has spread. Chemotherapy after surgery can help kill any remaining cancer cells and lower the chance of the cancer returning.
New therapies are being tested all the time. Hormone therapy uses estrogen to fight ovarian cancers that are sensitive to that hormone. PARP inhibitor therapy targets the genes of mutant cancer cells. Immunotherapy uses your immune system to attack cancer cells. Although these new ovarian cancer treatments show promise, they can be expensive and aren’t always fully covered by insurance.
FAQs
-
What age is most common for ovarian cancer patients?
Most cases of ovarian cancer are found in women aged 55 and older, with the average age at diagnosis being 62 years. Many women don’t realize that their risk of developing ovarian cancer increases with age and remains significant after menopause. Some assume they’re no longer at risk once their periods stop and may ignore symptoms that should be checked out. However, it’s still possible to develop the disease at any age.
-
How is ovarian cancer triggered?
Abnormal cells may appear in or around your ovaries. It isn’t clear how or why they form, but researchers believe genetic mutations, hormonal and environmental factors, and long-term exposure to harmful chemicals in products like hair relaxers and talcum powder may all contribute to increasing your risk.
-
Is ovarian cancer genetic?
Yes, genetic factors may contribute to ovarian cancer. About 25% of ovarian cancer cases are likely related to inherited genes. Exposure to chemicals can also increase your risk of developing genetic mutations that trigger cancerous cells. Once this happens, these cells can grow out of control and spread throughout your body.
-
Can you get ovarian cancer without being exposed to products like talc and hair relaxer?
Yes, you can develop ovarian cancer without being exposed to products that contain chemicals linked to increased risk. A combination of inherited genes, hormonal changes, your lifestyle and other factors contribute to your overall risk of developing the disease. Certain inherited genes, particularly BRCA1 and BRCA2, may increase your risk of developing some cancers, including ovarian cancer.
Meet the experts behind the article

Written by:
Lisa Merriam
Lisa Merriam is an experienced copywriter specializing in medical content, combining technical precision with clarity to ensure articles are accessible and accurate.

Medical review by:
Dr. Danielle K. Miller, DNP, MSN, BSN, RN
Danielle Miller brings more than two decades of expertise at the intersection of healthcare, education, and advocacy to her roles. As a doctorate-prepared nurse, certified birth and postpartum doula, and current law student, Danielle specializes in creating evidence-based yet empathetic content that empowers families navigating complex medical-legal issues.

Legal review by:
Jamie Pfeiffer, JD
Jamie L. Pfeiffer is a retired attorney with extensive experience litigating large-scale asbestos and toxic tort cases in Illinois, Oregon, and Washington. She brings a wealth of legal expertise to reviewing articles about toxic exposure and legal accountability in mass torts.

